Air Quality Features in the New LEED V5 Release
The LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification system, known for setting the global standard in green building design, has introduced significant updates in its latest version, LEED V5.
A key focus of this release is the enhancement of air quality criteria, reflecting the growing importance of indoor and outdoor air quality in sustainable building practices. Airscan team prepared a summary of the key updates came in action with the most recent LEED protocol.
Table of Contents
Fundamental Air Quality
The new version of the Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design protocol flags the importance of ventilation in a recently built buildings including investigation of the ambient air quality around a project site to minimize the risks of air pollution infiltration from an outdoor to an indoor environment.
To tackle these issues the new LEED v5 set a prerequisite of a Fundamental Air Quality assessment which covers:
- Outdoor Air Quality Assessment following ASHRAE Standard 62.1-2022
- Implement MERV 13 filter media or an equivalent solution
- Add a stand-alone in-room air purification systems if necessary
- Provide an outdoor airflow meter for all mechanical ventilations systems with air intake greater than 472 L/s
Air Quality Testing and Monitoring
The new LEED certification version allows to gain up to 2 extra points if an air quality testing and monitoring management plan is introduced in a project. The testing should cover two main air pollution groups:
Particulate Matter and Inorganic Gases
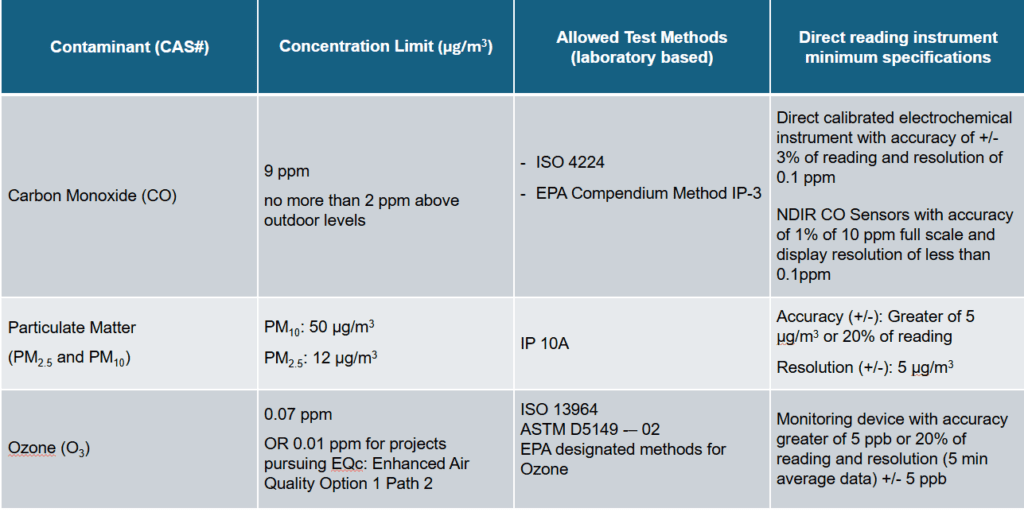
This part of the indoor air quality assessment covers measurements of Carbon Monoxide (CO) and Ozone (O3) gasses as well as Particulate Matter (PM2.5 & PM10). The measurements can be carried out following both Laboratory based methods as well as direct read instruments as given in the table below :
Contaminant (CAS#) | Concentration Limit (µg/m3) | Allowed Test Methods (laboratory based) | Direct reading instrument minimum specifications |
Carbon Monoxide (CO) | 9 ppm no more than 2 ppm above outdoor levels |
| Direct calibrated electrochemical instrument with accuracy of +/- 3% of reading and resolution of 0.1 ppm NDIR CO Sensors with accuracy of 1% of 10 ppm full scale and display resolution of less than 0.1ppm |
Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10) | PM10: 50 μg/m3 PM2.5: 12 μg/m3 | IP 10A | Accuracy (+/-): Greater of 5 μg/m3 or 20% of reading Resolution (+/-): 5 μg/m3 |
Ozone (O3) | 0.07 ppm OR 0.01 ppm for projects pursuing EQc: Enhanced Air Quality Option 1 Path 2 | ISO 13964 ASTM D5149 -– 02 EPA designated methods for Ozone | Monitoring device with accuracy greater of 5 ppb or 20% of reading and resolution (5 min average data) +/- 5 ppb |
Air Quality Testing and Monitoring
Volatile Organic Compounds
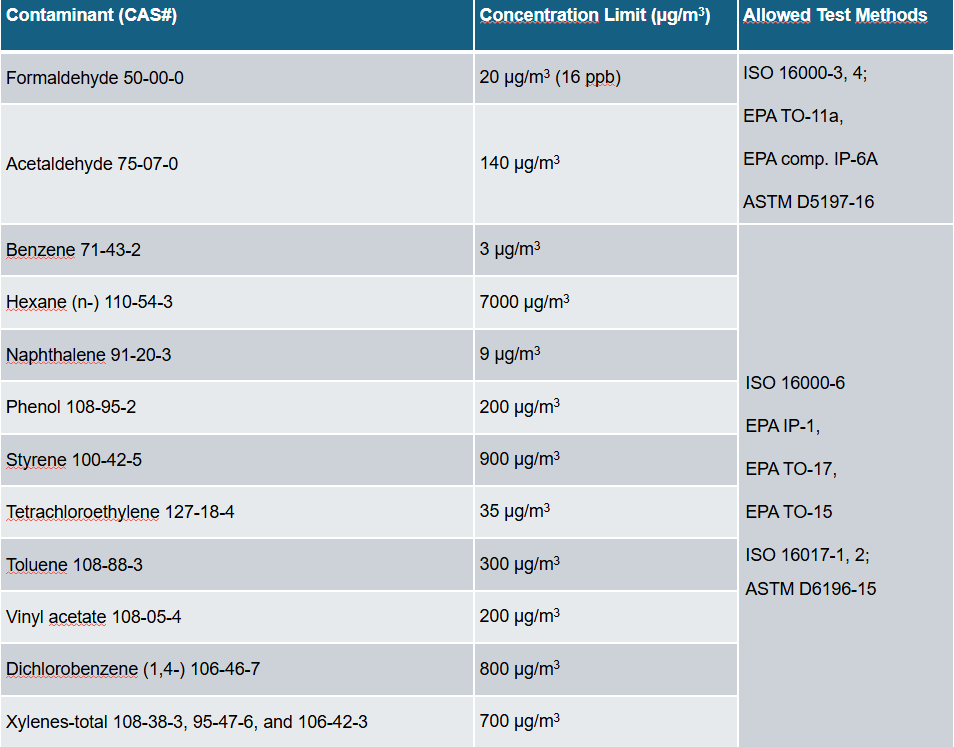
The second part of post-construction indoor air quality assessment covers sampling and analysis of Total and Individual Volatile Organic Compounds which must done by a party having ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation.
A full list of individual VOCs to be tested following the most recent LEED v5 guidebook and the required test methods are given below :
Contaminant (CAS#) | Concentration Limit (µg/m3) | Allowed Test Methods |
Formaldehyde 50-00-0 | 20 µg/m3 (16 ppb) | ISO 16000-3, 4; EPA TO-11a, EPA comp. IP-6A ASTM D5197-16 |
Acetaldehyde 75-07-0 | 140 µg/m3 | |
Benzene 71-43-2 | 3 µg/m3 | ISO 16000-6 EPA IP-1, EPA TO-17, EPA TO-15 ISO 16017-1, 2; ASTM D6196-15 |
Hexane (n-) 110-54-3 | 7000 µg/m3 | |
Naphthalene 91-20-3 | 9 µg/m3 | |
Phenol 108-95-2 | 200 µg/m3 | |
Styrene 100-42-5 | 900 µg/m3 | |
Tetrachloroethylene 127-18-4 | 35 µg/m3 | |
Toluene 108-88-3 | 300 µg/m3 | |
Vinyl acetate 108-05-4 | 200 µg/m3 | |
Dichlorobenzene (1,4-) 106-46-7 | 800 µg/m3 | |
Xylenes-total 108-38-3, 95-47-6, and 106-42-3 | 700 µg/m3 |
Continuous Indoor Air Monitoring
Welcoming a continuous indoor air quality monitoring solutions is the key update for the air section introduced by the LEED certification in the v5 release. The permanent air quality measurement devices should cover at least Carbon dioxide (CO2), Particulate Matter (PM2.5), Total Volatile Organic Compounds (TVOCs) and Comfort Parameters (T oC and RH %).
However, the guidelines lack specificity regarding sensor specifications, sampling frequency, and actionable steps based on collected data, which Airscan team believe should be more specific in the following releases.

Enhanced Air Quality
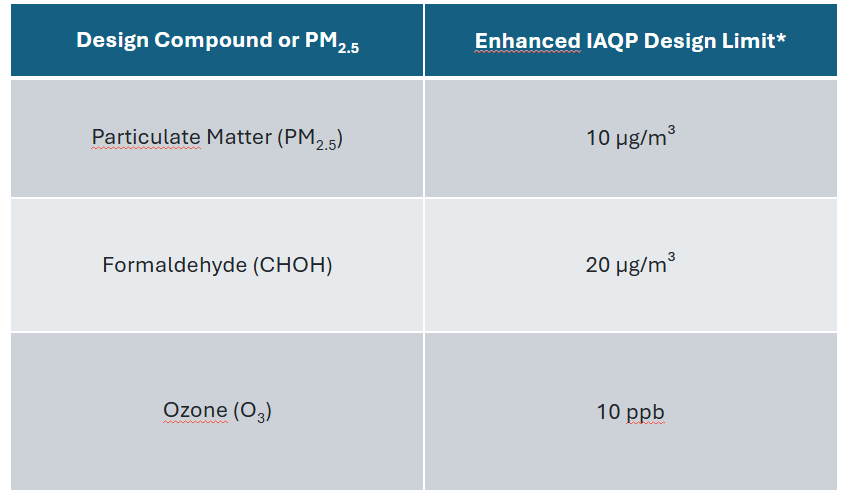
In addition to the fundamental air quality analysis, LEED v5 protocol provides an extra points for project meeting more strict threshold limits for specific compounds like Particulate Matter, Ozone and Formaldehyde as given in the table below.
Design Compound or PM2.5 | Enhanced IAQP Design Limit* |
Particulate Matter (PM2.5) | 10 µg/m³ |
Formaldehyde (CHOH) | 20 µg/m³ |
Ozone (O3) | 10 ppb |
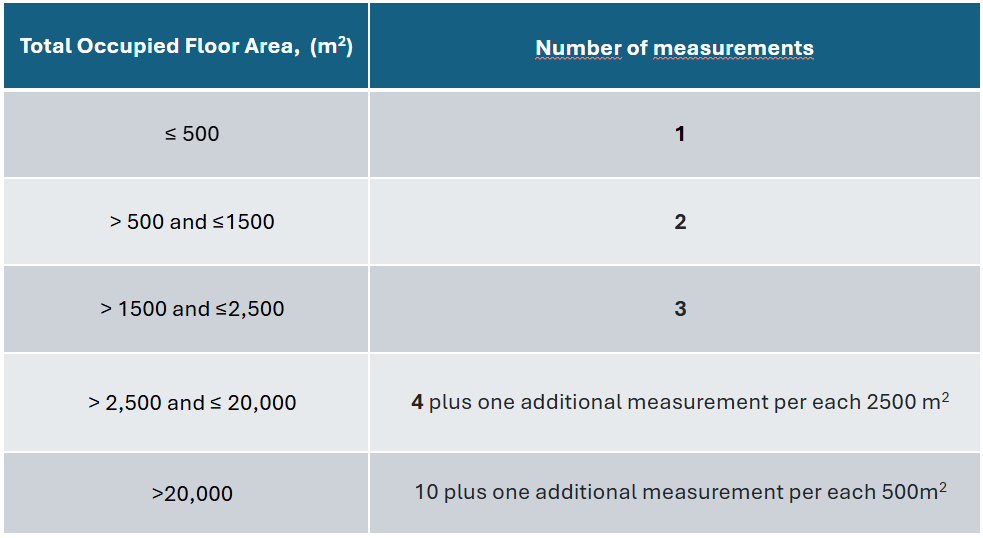
The last, but not least, the recent guidebook specifies the number of sampling points to be tested setting a clear requirement for developing a sampling campaign prior to initiating the indoor air quality management plan. The number of sampling points is directly proportional to the surface area of a project.
Total Occupied Floor Area, (m2) | Number of measurements |
≤ 500 | 1 |
> 500 and ≤1500 | 2 |
> 1500 and ≤2,500 | 3 |
> 2,500 and ≤ 20,000 | 4 plus one additional measurement per each 2500 m2 |
>20,000 | 10 plus one additional measurement per each 500m2 |
Conclusion
LEED v5 introduces pivotal changes in air quality standards that aim to create healthier, more sustainable indoor environments. By focusing on better filtration, continuous monitoring, and stringent testing of pollutants, this new version reflects the growing importance of air quality in building design.
While the updates are a step forward, further clarification on sensor specifications and data management will likely enhance their effectiveness in future releases. As the world continues to prioritize well-being and sustainability, these LEED guidelines pave the way for healthier, more sustainable and smarter buildings.
Latest Articles

School air quality: protect children today | Airscan
Children are more vulnerable to air pollution at school. Key Brussels data, effective measures (school streets, LEZ), and Airscan solutions: monitoring, smart ventilation, certification‑ready reporting.


Ventilation Audits in Flanders Care Homes: Airscan’s 40‑Site Study on Indoor Air Quality
Airscan’s audit of 40 Flemish care homes uncovered critical ventilation issues: nearly 1 in 4 rooms exceeded safe CO₂ limits. With VEB and VIPA support, the study offers data-driven solutions to protect residents’ health.
